Acne: Acne Causes, Acne Types, Acne Treatment and Tips
Dr Aastha Gupta, award winning dermatologist from AIIMS says that “Acne often causes poor self-image, depression and anxiety to the person afflicted by the condition. Early and adequate treatment in moderate and severe acne cases prevents sequelae such as pigmentation and scarring. Chemical peels such as glycolic acid and salicylic acid, microdermabrasion, CO2 laser therapy and dermaroller treatments can reduce the acne lesions, improve the texture of the skin and reduce the scars and pigmentation and these treatments are available at Kailah hospital.”
What is Acne?
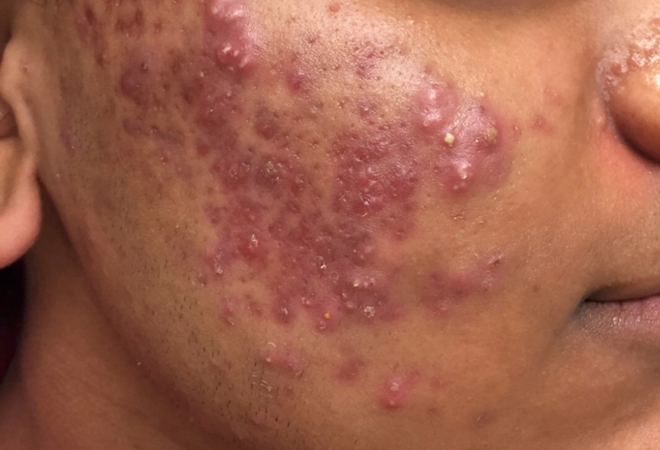
Acne (or pimples) is an inflammatory skin disease that usually starts at puberty and mainly affects the teens and young adults. It presents as comedones (blackheads and whiteheads), red raised lesions, pus-filled lesions or painful swellings. The lesions are seen primarily involving the face, but can also occur on the arms, back & chest.
What causes acne?
The key events in causation of acne include excess sebum (oil) production in the skin, formation of a plug at the outlet of the skin pores (pilosebaceous unit) with dead cells and bacteria leading to the appearance of black heads (open comedones) and whiteheads (closed comedones) and overgrowth of the bacteria (P.Acnes) causing inflammation in the pilosebaceous unit which leads to the formation of red raised lesions, pus filled lesions and cysts.
What are factors that aggravate Acne?
Emotional and physical stress, procedures such as oil massage, facials and clean- ups and use of oil based cosmetics and scrubs can aggravate acne. Abuse of topical steroid creams on the face often promoted as fairness creams can cause adverse effects including acne. Also certain drugs like steroids, anti-tubercular medicines (isoniazid), anti-epileptics (phenobarbitone) can cause Acne like eruptions.
What is hormonal acne?
Sometimes acne may be a sign of underlying hormonal disease such as polycystic ovarian syndrome(PCOS). PCOS is characterized by presence of multiple cysts in the ovaries leading to irregular menstrual cycles, weight gain, thinning of hair on the scalp and excessive hair on the face. These patients usually have acne along the jawline which may be severe and may be accompanied by premenstrual flares. Also, acne persisting beyond the age of 25 years or starting after this age (known as adult or late-onset acne) may indicate the presence of hormonal disturbances.
What is the role of diet in acne?
Diet is an important factor in aggravating Acne. High caloric (glycemic) foods such as pastries and sweets and dairy products like cheese, paneer, butter & ghee can trigger or worsen the existing Acne. Whey protein, used by adults engaged in body-building sports is also implicated in aggravation of Acne. Healthy food habits, fresh vegetables & fruits and lots of water help in maintaining a healthy skin.
What should one do if he/she gets Acne? When should you visit a dermatologist?
Acne may resolve or subside over time. However, it may not clear on its own and may produce pus- filled lesions and large swellings which may leave permanent disfiguring scars, if left untreated. Consulting a dermatologist early in the course of disease can prevent further worsening of the disease and also reduce the chances of post acne hyperpigmentation and scarring.
How should one take care of an Acne prone skin?
- Wash the face 2-3 times daily with preferably a soap-free cleanser and water.
- The scalp should be cleansed 2-3 times weekly to prevent and remove dandruff.
- Avoid all greasy cosmetics on the face. Look for a ‘non comedogenic’ cosmetic which is safer in acne prone skin.
- Do not squeeze or pick the pimples. It can cause scarring.
What are the treatment modalities for Acne?
The treatment of acne depends on the predominant type of lesions and the presence of sequelae such as hyperpigmentation and scarring. For mild cases containing mainly comedones and few papules topical medications (applied to the skin) such as benzoyl peroxide, retinoids, azelaic acid, antibiotic creams (clindamycin) are recommended. For moderate to severe cases oral medications such as antibiotics (azithromycin, doxycycline, minocycline & tetracyclines), retinoids (isotretinoin) and hormonal therapy (oral contraceptive pills, anti-androgens.systemic) are usually advised. Most patients may require a combination of both therapies. Some patients may also require chemical peel, laser and other technologies for faster and effective treatment. Chemical peels such as glycolic acid and salicylic acid peels reduce the acne lesions, improve the texture of the skin and reduce the pigmentation. Treatments effective for improving acne scars include microdermabrasion, derma roller, laser (fractional lasers) and subcision. Keloidal scars may need intralesional injections or cryotherapy.
If you are suffring from Acne Problem then you can Book an appoinment here: Best Dermatologist in Noida